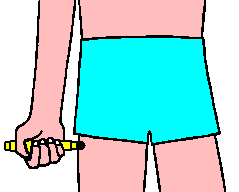| |
Epipen Details
Clinical InformationNotice
Bearing
in mind the content of this page it would be sensible to source
information elsewhere. I am not qualified to decide if the information
here is correct or not and suggest you visit the Epipen website.
Roger Patterson. Website Administrator
|
|---|

EPIPEN 0.3 mg EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR
for Intramuscular Injection of
Epinephrine. For the Emergency Treatment of Allergic Reactions
(Anaphylaxis), the device Delivers 0.3 mg intramuscular dose of
epinephrine from Epinephrine Injection, USP, 1:1000 (0.3 ml).
DESCRIPTION The EpiPen Auto-Injector contains 2 ml Epinephrine Injection for
emergency intramuscular use. Each EpiPen Auto-Injector delivers a single dose of
0.3 mg epinephrine from Epinephrine Injection. USP. 1:1000 (0.3 ml) in a sterile
solution.
For stability purposes. approximately 1.7 ml remains in the Auto-Injector after
activation. Each 0.3 ml contains 0.3 mg epinephrine. 1.8 mg sodium chloride.
0.5 mg sodium metabisulfite. hydrochloric acid to adjust pH. and Water for Injection
The pH range is 2.5-5.0
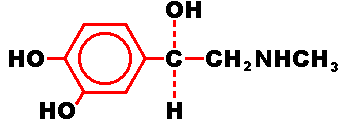
Epinephrine is a sympathomimetic catecholamine. Chemically, epinephrine is B-(3,
4-dihydroxyphenyl)-a-methylaminoethanol. with the following structure.
It deteriorates rapidly on exposure to air or light. turning pink from oxidation to
adrenochrome and brown from the formation of melanin EpiPen Auto-Injectors whose contents
show evidence of discolouration should be replaced.
CLINlCAL PHARMACOLOGY Epinephrine is a sympathomimetic drug.
acting on both alpha and beta receptors. It is the drug of choice for
the emergency treatment of severe allergic reactions (Type 1) to
insect stings or bites, foods, drugs, and other allergens. It can
also be used in the treatment of idio-pathic or exercise-induced
anaphylaxis. Epinephrine when given subcutaneously or intramuscularly
has a rapid on-set and short duration of action. The strong
vasoconstrictor action of epinephrine through its effect on alpha
adrenergic receptors acts quickly to counter vasodilation and
increased vascular permeability which can lead to loss of
intravascular fluid volume and hypotension during anaphylactic
reactions. Epinephrine through its action on beta receptors on
bronchial smooth muscle causes bronchial smooth muscle relaxation
which alleviates wheezing and dyspnea. Epinephrine also alleviates
prurilis, urticaria, and angioedema and may be effective in relieving
gastrointestinal and genitourinary symptoms associated with
anaphylaxis.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Epinephrine is indicated in the
emergency treatment of allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) to insect
stings or bites, foods, drugs and other allergens as well as
idiopathic or exercise-induced anaphylaxis. The EpiPen Auto-Injector
is intended for immediate self administration by a person with a
history of an anaphylactic reaction. Such reactions may occur within
minutes after exposure and consist of flushing, apprehension, syncope,
tachycardia, thready or unobtainable pulse associated with a fall in
blood pressure, convulsions, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal cramps.
involuntary voiding, wheezing, dyspnea due to laryngeal spasm,
pruritis, rashes, urticaria or angioedema. The EpiPen is designed as
emergency supportive therapy only and is not a replacement or
substitute for immediate medical or hospital care.
CONTRAINDlCATIONS There are no absolute contraindications to
the use of epinephrine in a life-threatening situation.
WARNINGS Epinephrine is light sensitive and should be stored
in the tube provided. Store at room temperature (15-30 degrees C,
59-86 degrees F). Do not refrigerate. Before using, check to make
sure solution in Auto-Injector is not discoloured. Replace the
Auto-Injector if the solution is discoloured or contains a
precipitate. Avoid possible inadvertent intravascular administration.
Select an appropriate injection site such as the thigh.
DO NOT INJECT INTO BUTTOCK.
Large doses or accidental intravenous injection of epinephrine may
result in cerebral haemorrhage due to sharp rise in blood pressure.
DO NOT INJECT INTRAVENOUSLY.
Rapidly acting vasodilators can
counteract the marked pressor effects of epinephrine.
Epinephrine is the preferred treatment for serious allergic or other
emergency situations even though this product contains sodium
metabisulfite. a sulfite that may in other products cause
allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms or
life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain
susceptible persons. The alternatives to using epinephrine in a
life-threatening situation may not be satisfactory. The presence of
a sulfite in this product should not deter administration of the drug
for treatment of serious allergic or other emergency situations.
Accidental injection into the hands or feet may result in loss of blood
flow to the affected area and should be avoided. If there is an
accidental injection into these areas, advise the patient to go
immediately to the nearest emergency room for treatment.
|
EpiPen should only be injected into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh.
| |
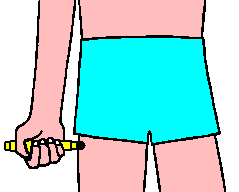
|
|---|
PRECAUTIONS Epinephrine is essential for the treatment of
anaphylaxis. Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions
(anaphylaxis) to insect stings or bites, foods, drugs, and other
allergens as well as idiopathic and exercise induced anaphylaxis
should be carefully instructed about the circumstances under which
this life-saving medication should be used. It must be clearly
determined that the patient is at risk of future anaphylaxis. Since
the following risks may be associated with epinephrine administration
(see Dosage and administration).
Epinephrine is ordinarily administered with extreme caution to patients
who have heart disease. Use or epinephrine with drugs that may
sensitize the heart to arrhythmias, e.g., digitalis, mercurial
diuretics, or quinidine, ordinarily is not recommended. Anginal pain
may be induced by epinephrine in patients with coronary insufficiency.
The effects or epinephrine may be potentiated by tricyclic
antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
Hyperthyroid individuals. individuals with cardiovascular disease,
hypertension, or diabetes, elderly individuals. pregnant women, and
children under 30 kg (66 lbs) body weight may be theoretically at
greater risk of developing adverse reactions after epinephrine
administration.
Despite these concerns, epinephrine is essential for the treatment of
anaphylaxis. Therefore, patients with these conditions, and/or any
other person who might be in a position to administer EpiPen or
EpiPen Jr. to a patient experiencing anaphylaxis should be carefully
instructed in regard to the circumstances under which this
life-saving medication should be used.
CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS, IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
Studies or epinephrine in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic and
mutagenic potential or the effect on fertility have not been
conducted. This should not prevent the use or this life-saving
medication under the conditions noted under INDICATIONS AND USAGE and
as indicated under PRECAUTIONS above.
USAGE IN PREGNANCY
Pregnancy Category C... Epinephrine has been shown to be teratogenic
in rats When given in doses about 25 times the human dose. There are
no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women.
Epinephrine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential
benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
PEDIATRIC USE Epinephrine may be given safely to children at a
dosage appropriate to body weight (see Dosage and Administration).
ADVERSE REACTIONS Side effects or epinephrine may include
palpitations, tachycardia, sweating, nausea and vomiting, respiratory
difficulty, pallor, dizziness, weakness, tremor, headache,
apprehension, nervousness and anxiety.
Cardiac arrhrythmias may follow administration of epinephrine.
OVERDOSAGE or inadvertent intravascular injection of
epinephrine may cause cerebral haemorrhage resulting from a sharp rise
in blood pressure. Fatalities may also result from pulmonary oedema
because of peripheral vascular constriction together with cardiac stimulation,
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION A physician who prescribes EpiPen
should take appropriate steps to ensure that the patient understands
the indications and use of this device thoroughly. The physician
should review with the patient or any other person who might be in
a position to administer EpiPen or EpiPen Jr. to a patient
experiencing anaphylaxis, in detail, the patient instructions and
operation of the EpiPen Auto-InJector. Inject the delivered dose of
the EpiPen Auto-Injector (0.3 mL Epinephrine Injection. USP. 1:1000)
intramuscularly into the anterolateral aspect of the thigh, through
clothing if necessary. See detailed Directions for Use on the
accompanying Patient Instructions.
Usual epinephrine adult dose for allergic emergencies is 0.3 mg. For
pediatric use, the appropriate dosage may be 0.15 or 0.30 mg depending
upon the body weight of the patient (see labeling for EpiPen Jr.).
However, the prescribing physician has the option of prescribing
more or less than these amounts, based on careful assessment of each
individual patient and recognizing the life-threatening nature of the
reactions for which this drug is being prescribed. The physician
should consider using other forms of injectable epinephrine if lower
doses are felt to be necessary for small children.
With severe persistent anaphylaxis, repeat injections with an
additional EpiPen may be necessary.
Parenteral drug products should be periodicaly inspected visually by
the patient for particulate matter or discolouration and should be
replaced if these are present.
HOW SUPPLIED EpiPen Auto-Injectors (Epinephrine Injection.
USP. 1:1000, 0.3 ml) are available singly or in packages of twelve
(pharmacy pack). NDC 0268-0301-01. Store in a dark place at room
temperature (15 - 30 degrees C, 59 -86 degrees F).
Do not refrigerate.
CAUTION: Federal (U.S.A) law (and UK Law) prohibits dispensing without a prescription.
This page has been prepared from a leaflet originally produced by
Center Laboratories, Washington, USA, printed in 1993.
Written... 17 August 2001,
Revised... 06 March 2002,
Upgraded... 15 November 2005, Revised 30-11-11,
|